Vinyl acetate: Pharmacodynamics, Toxicity, Applications, Preparation
Introduction
Vinyl acetate is a colorless liquid with a sweet smell. It is an important chemical used in the production of many different materials, including paints, adhesives, and coatings. Vinyl acetate is also used to make polyvinyl acetate (PVA), a type of glue commonly used in woodworking and paper crafts. Additionally, vinyl acetate can be polymerized to produce polyvinyl acetate resins, which are used in a variety of applications such as coatings, textiles, and packaging materials. The polymerization process can be controlled to produce different molecular weights and properties, allowing for a wide range of applications. However, vinyl acetate is considered to be a hazardous substance and should be handled with care[1].

Figure 1 Appearance of Vinyl acetate
Pharmacodynamics
If people are prolonged exposure to Vinyl acetate can cause damage to the respiratory system, liver, kidneys, and central nervous system, and may lead to cellular and tissue-level pathological changes such as cancer when severe. Vinyl acetate can also cause allergic reactions, manifested as skin irritation, difficulty breathing, dizziness, nausea, and other symptoms. In addition, Vinyl acetate can be broken down into acetic acid and ethylene, both of which have some biological activity within the body. Overall, due to the incomplete understanding of the metabolism and mechanisms of action of Vinyl acetate in the human body, its use as a conventional drug is not recommended.
Toxicity
Vinyl acetate is primarily used in the manufacture of polyvinyl acetate and polyvinyl alcohol, which are commonly used in adhesives, coatings, and films. Vinyl acetate can be toxic if it is inhaled, ingested, or comes into contact with the skin or eyes. Inhalation of vinyl acetate vapor can cause irritation to the respiratory system and eyes, coughing, wheezing, and headache. Prolonged exposure may cause lung damage or cancer. If vinyl acetate is ingested, it can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. It may also cause liver and kidney damage in severe cases. When vinyl acetate comes into contact with the skin, it can cause irritation, redness, and blisters. Chronic exposure to vinyl acetate may lead to skin sensitization and an increased risk of developing contact dermatitis.
Overall, vinyl acetate should be handled with care and proper precautions should be taken to minimize exposure. Appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn, and exposure limits should be strictly followed to prevent toxicity[2].
Applications
Vinyl acetate is a monomer that has numerous applications. One of the most significant uses of vinyl acetate is in the production of polyvinyl acetate (PVA), which is used in adhesives, paints, and coatings. Vinyl acetate is also used to produce other polymers, such as ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which is used in hot melt adhesives, wire and cable insulation, and footwear. Additionally, vinyl acetate is used in the production of vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymers, which are used in packaging films, automotive interiors, and upholstery fabrics. The textile industry also utilizes vinyl acetate for the production of water-soluble films and fibers. Overall, vinyl acetate has an array of applications across several industries due to its versatility and unique properties.[3-8].
Preparation
Vinyl acetate is a colorless liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. It is primarily used in the production of polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and other vinyl-based polymers.
The preparation of vinyl acetate involves the reaction between ethylene, acetic acid, and oxygen over a palladium catalyst:
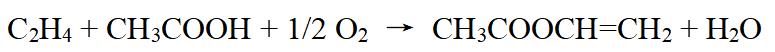
Figure 2 chemical reaction formula of Vinyl acetate
This reaction takes place under controlled conditions of temperature, pressure, and concentration to ensure the highest possible yield of vinyl acetate. The process usually occurs in several stages, including the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde, the reaction of acetaldehyde with acetic acid to form ethylidene diacetate, and then the dehydrogenation of ethylidene diacetate to produce vinyl acetate.
Vinyl acetate can also be produced by esterification of acetic acid with acetylene in the presence of a mercury(I) salt catalyst:
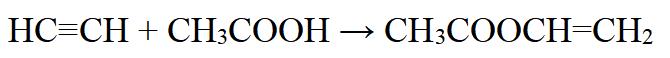
Figure 3 chemical reaction formula of Vinyl acetate
However, this method is less commonly used due to safety concerns associated with the use of acetylene.
References
[1] Yin, H., Xu, Y. Synthesis of poly(vinyl acetate) using a novel emulsifier-free miniemulsion polymerization technique.[J] Journal of Polymer Research. 2019, 26(2), 1-11.
[2] Rusyn, I., et al. Vinyl acetate: a case study in the application of the threshold of toxicological concern (TTC) for assessing environmental and human health risk implications of impurities in industrial chemicals. Critical Reviews in Toxicology. 2004, 34(3), 261-289.
[3] Wang C., Xie Y., Gao P., et al. Synthesis and Application of Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) Adhesive. Fine Chemicals, 2010, 27(10): 1011-1014.
[4] Mahdi H., Piri F., Hosseinzadeh S., et al. Thermal properties and crystallization behavior of EVA/PMMA blends with different compositions. Materials & Design, 2013, 44: 120-126.
[5] Gao J., Chen Y., Chen C., et al. Properties of waterborne polyurethane/vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer composite emulsion coatings. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2016, 95: 119-125.
[6] Ma N., Qi M., Zeng G.P. Structure and properties of polylactic acid textile modified by vinyl acetate. Journal of Textile Research, 2016, 37(4): 59-64.
[7] Zhang J., Li S., Liu Y.Z., et al. Development and application of vinyl acetate/n-butyl rubber composite ink. New Chemical Materials, 2019, 47(7): 184-187.
[8] Han X.M., Wu Q., Cai G.S. Study on the use of vinyl acetate copolymer-polyurethane coating for food packaging materials. Food Science and Technology, 2013, 38(3): 183-185.
);You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Vinyl acetate manufacturers

US $1.00/g2024-04-25
- CAS:
- 108-05-4
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99
- Supply Ability:
- 20tons

US $23.00/kg2024-02-27
- CAS:
- 108-05-4
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 5000 tons




